.png)

Evaluating the Effectiveness of Scenario Based Learning Using a Blended Approach Among Undergraduate Nursing Students
On This Page
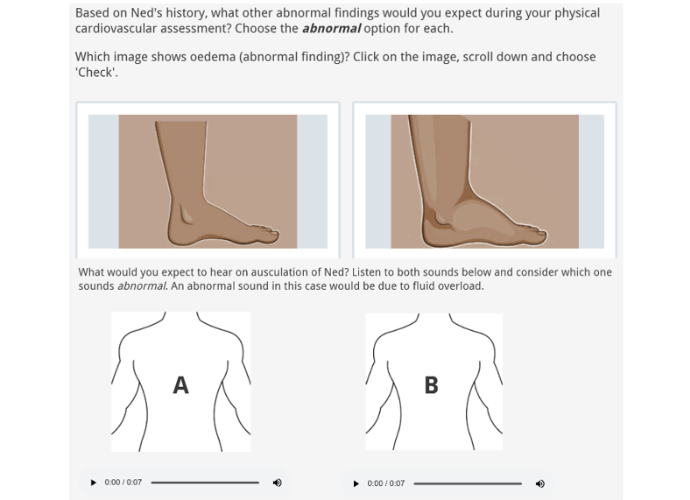
Introduction
While undergraduate education aims to provide student nurses with a level of competence for independent practice, criticisms exist surrounding the ability of these programmes to adequately prepare graduates for the clinical skills required to optimise care. Adopting virtual simulations into nursing curricula may support greater clinical preparedness. However, learning is also cited as a social experience requiring teacher-student interaction. Therefore, a challenge exists to develop teaching strategies that balance interactive learning while also ensuring students achieve relevant competencies. Using scenario-based learning in a blended environment, this research evaluated the impact of different teaching modalities (in-person vs virtual patient case simulations) on undergraduate student nurses' perceived learning gains and self-efficacy.
Project Outline
Results from the pre-test-post-test emphasised students' positive perceptions for both teaching modalities. However, following participation with virtual simulation, significant, positive improvements were identified. Three key themes were generated from open-ended survey responses which revealed the core features of both teaching modalities and students' desire to further integrate more virtual activities into undergraduate curricula.
By combining the advantages of in-person and online learning platforms, a blended approach can close the theory to practice gap and support diverse student cohorts to succeed within nursing education.
Project Outputs
Rogers L. & MacCormac A. (2025). Finding a balance: Using a pre-post test to evaluate the effectiveness of scenario based learning using a blended approach among undergraduate nursing students. Nurse Education Today, 147 (Article 106573)
Project Team
.png)
.png)
